Antibiotics are a staple of modern medicine to treat life-threatening bacterial infections. However, many people are hesitant to take them because they fear the side effects. In particular, they worry that antibiotics might lead to bacterial resistance and cause skin irritation.
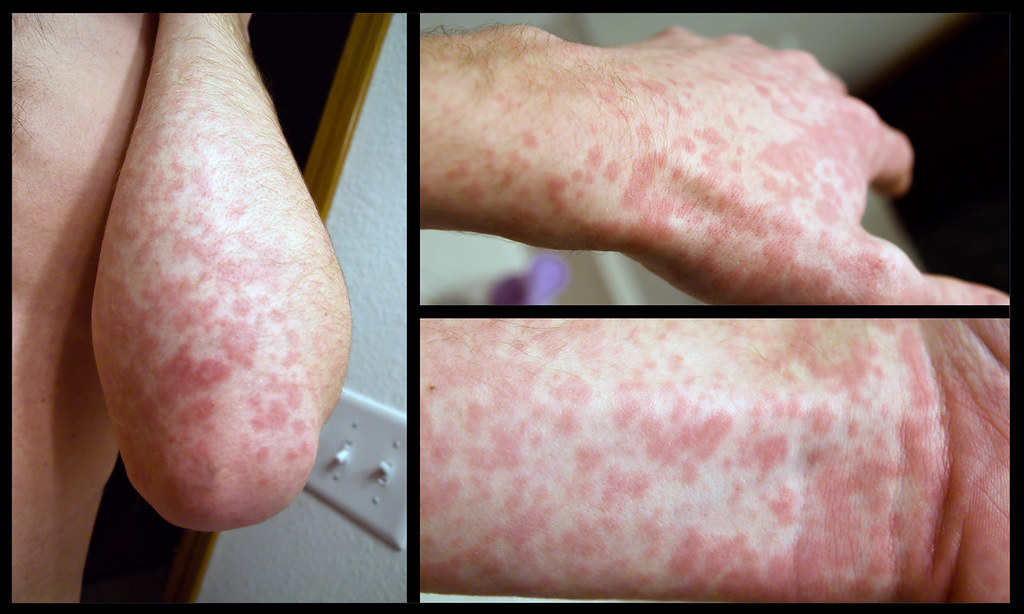
Fortunately, most antibiotics do not pose a risk of skin irritation. However, the ones that do may cause redness, peeling, and itching.
Visit the website https://wellnessadvice.info/if you do want to know more about how to take better care of your skin irritation.
In this article, you will learn about the types of antibiotics and their potential side effects. You will also learn how to find an antibiotic that does not cause skin irritation. Keep reading to learn more about how to find an antibiotic that doesn’t cause skin irritation.
What Is Skin Irritation?
Image Source: Flickr
Skin irritation occurs when a medication causes redness, peeling, or itching on the skin. These side effects are common when people take antibiotics. These side effects are not caused by the bacteria or bacteria’s effect on the skin. Instead, they occur as a result of the medications that kill the bacteria. For this reason, it’s recommended to consult with a Philadelphia dermatology care provider prior to using any products on your skin.
However, not all antibiotics cause skin irritation. In fact, only a small number of antibiotics actually do. The reason many antibiotics cause skin irritation is that they affect different parts of the skin. Some antibiotics affect the outermost layer of the skin called the epidermis and then cause irritation when they get into the dermis. To avoid this side effect, it is important to use an antibiotic only for the time prescribed by your doctor.
Why Do Some Antibiotics Cause Skin Irritation?
Antibiotics kill bacteria by disrupting their normal growth and metabolism. One of the ways bacteria grow is by producing a type of acid that can harm the skin. When taking an antibiotic, the acid levels in the skin increase. This causes the skin to become dry and crusty. Dry, itchy skin is the most common side effect of taking an antibiotic. Dry skin occurs because the bacteria that cause bacteria-induced rash (dermatitis) also produce an oily substance that can lead to itching. In addition to itching, dry skin can make it difficult to treat certain infections.
How to Find an Antibiotic That Does Not Cause Skin Irritation
You may be wondering how to find an antibiotic that does not cause skin irritation. Start by asking your doctor if there are any antibiotics that do not cause skin irritation. If you are prescribed an antibiotic that causes skin irritation, don’t be afraid to ask your doctor to recommend a different option. As mentioned above, not all antibiotics cause skin irritation.
By asking your doctor, you can avoid the risk of irritating your skin while ensuring that you receive the treatment that is right for you. You must have knowledge about the causes of skin irritation, visit the website https://www.egmedicine.com/ to know about it.
Tips to Avoid Antibiotic-Related Skin Irritation
If you are taking an antibiotic, it’s important to use it exactly as prescribed. You can avoid antibiotic-related skin irritation by following these guidelines:
- Don’t stop taking your medication abruptly. When you finish taking an antibiotic, it’s important to have a wait-and-see approach. Your body may need time to heal without the help of the medication. Your doctor will likely recommend that you stay on antibiotics for 2-4 weeks after any serious infection resolves. However, it is important that you don’t stop taking the medication after you are done with treatment.
- Wear sunscreen while you are taking an antibiotic. Sunscreen protects your skin from the sun and helps to prevent dry, itchy skin. So make sure to use sunscreen while you are on an antibiotic.
- Don’t use fragrances or moisturizers in the area around your mouth (for example, under your nose or between your toes). These products can get into your bloodstream and may make your side effects worse.
- Wash your hands frequently to prevent bacterial infections that are spread from person to person through contact.
- Ask your doctor if you should avoid specific foods or drinks while you are taking an antibiotic.
- Keep your medications in a place that is easy to access (such as near the bed or in your medicine cabinet). Having everything you need to take your medication is important for avoiding side effects and saving time.
- Report any side effects as soon as they occur. This will help your doctor quickly diagnose the source of your irritation and recommend appropriate solutions.